Phylum – Porifera – (Pore-bearing)
Introduction: The porifers are commonly known as sponges. Porifers consisting the most primitive multicellular animals. These are pore-bearing animals, the body does not consist of organs and they can regenerate their lost parts.
The phylum includes around 5ooo species. These are the first multicellular animals. They are called sponges because of their spongy appearance. They show a symbiotic relationship with algae.
Characteristic features of phylum Porifera:
- Habitat: The members of this phylum are generally marine and some are found in freshwater.
- Level of Organisation: Cellular level of organization. (These are primitive Multicellular animals). The cells are loosely organized.
- Symmetry: these are found mostly in asymmetrical animals.
- Water transport or canal system –
- Sponges consist of Water transport or canal system, water enters through a pore called Ostia.
- From Ostia, the water goes to the body wall into the central cavity that is called spongocoel from here the water goes out through the osculum.
- The function of the pathway of the water transport system
- This water transport pathway helps gather food.
- Respiratory exchange
- Removal of waste
- Choanocytes or collar cells: These function to line the spongocoel and canals.
- Digestive system: In sponges, They exhibit holozoic nutrition. The digestive system is found intracellular.
- Intracellular digestion: Breakdown of food or energy-providing substances within the cell.
- Skeleton: In Sponges, the body is supported by a skeleton. The skeleton is made up of Spicules or spongin fibers.
- Sexes: These are hermaphrodites (sexes are not separate), i.e. sperm and eggs are produced by the same individual.
- Reproduction
- Asexual reproduction: They reproduce asexually by fragmentation.
- Sexual reproduction: Formation of gametes takes place. In sponges, fertilization occurs internally.
- Indirect development is found in sponges during the larval stage and adult stages. The larval stage in porifers is morphologically distinct from the adult stage. The larva is ciliated and free-swimming, called parenchymulla and amphiblastula.
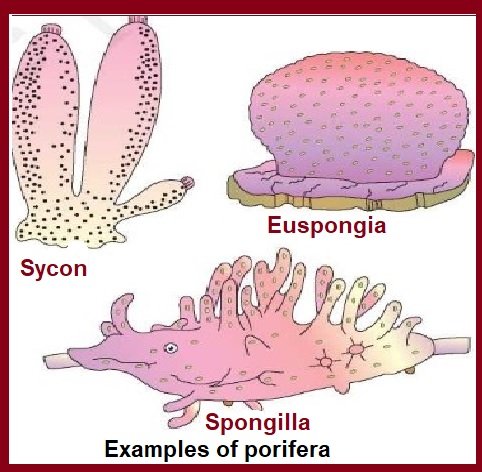
Examples of Porifera
- Sponge Cliona is detrimental to the pearl industry
- Spongiolla is an example of a freshwater sponge
Classification of Phylum Porifera
The phylum is classified into three classes these are:
Calcarea
- Habitat: Marine, shallow coastal water
- Body: skeleton is composed of calcareous spicules made up of calcium carbonate.
- Symmetry: They show radial symmetry, with cylindrical bodies.
- The organization of the body is asconoid, syconoid, or maybe leuconoid.
- Example: Clathrina, Scypha
Hexactinellids
- Habitat: Marine
- Skeleton made by six-rayed siliceous spicules.
- Symmetry: radial with shape cylindrical
- The Canal system is found in Sycon or Leucon
- Example: Euplectella, Hyalonema
Desmospongiae
- Habitat: Freshwater or Marine
- Body: asymmetrical and cylindrical in shape
- Leuconoid-type canal system
- Skeleton consists of spongin fibers, siliceous spicules, and are monoaxon and triaxon.
- Example: Spongia, Spongilla, etc.
Some examples of porifers: Sycon (Scypha), Euspongia (Bath sponge), Hylonema, and Spongilla (Freshwater sponge)
You can also read: 💡
- Phylum Coelenterata
- Phylum Ctenophora
- Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Phylum-Annelida
- Phylum-Arthropoda
- Phylum-Mollusca
- Phylum-Echinodermata
- Phylum-Chordata
Thank You 🙂



20 Comments
Classification of Animals- Phylum Aschelminthes to Hemichordata All Competitive Classes Science % - % · January 29, 2021 at 9:04 pm
[…] Echinodermata, and Hemichordata. As in the earlier blog, we’ve studied Phylum Porifera to Platyhelminthes and the basis of Classification of […]
All Competitive Classes Characteristics and Classification of Phylum Chordata Science - · February 4, 2021 at 7:03 pm
[…] the previous post, we studied the Classification of animals, Major phyla Phylum -Porifera, Coelenterata (Cnidaria), Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Aschelminthes, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata, and Hemichordata. In this blog, […]
Classification of Animals- Phylum Aschelminthes to Hemichordata Biology · March 16, 2021 at 5:46 pm
[…] Mollusca, Echinodermata, and Hemichordata. As in the earlier blog, we’ve studied Phylum Porifera to Platyhelminthes and the basis of Classification of […]
Animal kingdom PCSSTUDIES - Biology - Animal kingdom · March 16, 2021 at 6:02 pm
[…] Coelenterates, tissue level of organisation is […]
PCSSTUDIES - Characteristics and Classification of Phylum Chordata % - · April 2, 2021 at 5:41 pm
[…] the previous post, we studied the Classification of animals, Major phyla Phylum -Porifera, Coelenterata (Cnidaria), Ctenophora, Platyhelminthes, Aschelminthes, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata, and Hemichordata. In this blog, […]
Phylum - Coelenterata (Cnidaria) - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · May 29, 2021 at 6:36 am
[…] You can also read: Phylum porifera […]
Phylum- Ctenophora - PCSSTUDIES - Biology - Phylum- Ctenophora · May 29, 2021 at 7:22 am
[…] Phylum porifera […]
Phylum Aschelminthes - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % · May 29, 2021 at 3:39 pm
[…] Phylum – Porifera […]
Phylum-Annelida - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % Phylum-Annelida · May 29, 2021 at 4:29 pm
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Phylum-Mollusca - PCSSTUDIES - Biology - Phylum-Mollusca · May 29, 2021 at 7:04 pm
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Phylum-Echinodermata - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % · May 30, 2021 at 12:43 am
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Phylum-Hemichordata - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % · May 30, 2021 at 2:01 am
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Phylum-Arthropoda - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Phylum-Arthropoda · June 15, 2021 at 8:15 pm
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Amphioxus (Lancelet) - PCSSTUDIES - Science Amphioxus (Lancelet) · July 22, 2021 at 6:03 pm
[…] Phylum – Porifera […]
Blanoglossus - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Blanoglossus · August 9, 2021 at 10:53 pm
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Balanoglossus - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Balanoglossus · August 10, 2021 at 7:23 am
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Petromyzon (Lamprey): General Characters - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · November 19, 2021 at 10:35 pm
[…] Phylum – Porifera […]
Subphylum - Urochordata - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · November 19, 2021 at 11:05 pm
[…] Phylum – Porifera […]
Phylum- Platyhelminthes - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · September 15, 2022 at 1:03 pm
[…] Phylum Porifera […]
Taxonomy - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · November 28, 2023 at 8:14 pm
[…] Phylum – Porifera […]