Subphylum – Urochordata
Subphylum – Urochordata (Tunicates)
Subphylum – Urochordata: Position of Urochordates- Lamarck placed Tunicata in between radiate and Vermes in his system of classification. Later they were kept in Mollusca. Kowalevsky kept them in chordates in 1866.
The Urochordates are also known as tunicates. These are commonly known as “sea squirts”. The 1,300 species of urochordates are known.
Characteristic features of Urochordata
The Urochordates possess four characteristic anatomical structures as embryos:
- A flexible body-length rod notochord that provides resistance against muscular contractions and allows for more efficient movement;
- A dorsal, hollow, nerve cord that forms the central nervous system;
- Slits at the beginning of the digestive tract (the pharynx) that allow filter-feeding and gas exchange; and
- A post-anal tail.
General Characters of Urochordates:
They show features of chordates clearly in the larvae stage, while adults show more like invertebrates than chordates.
- The body shows variation in size and form.
- Unsegmented body, absence of a tail
- The body is covered by a test. It is formed by tunicine which is rallied to cellulose. Hence the name Tunicata
- The body wall of urochordates shows one layered epidermis, the dermis is made by connective tissue and muscles, and the atrial epithelium.
- Coelom is absent in tunicates.
- The atrial cavity surrounds the pharynx, and into this cavity, the gill slits, anus, and genital ducts will Open. It opens through the atrial aperture.
- In urochordates Ciliary mode of feeding is common
- The respiratory system in tunicates contains gills in the pharyngeal wall.
- The heart in tunicates is found as the Ventral heart
- The nervous system of tunicates is represented by a single dorsal ganglion in the adult
- Excretion in Urochordates is by nephrocytes
- In urochordates Asexual reproduction by budding.
- These are bisexual animals and cross-fertilization during reproduction.
- In urochordates fertilization is external.
Classes of Subphylum – Urochordata
Subphylum – Urochordata is divided into three classes:
- Class-Ascidiacea
- Class- Thaliacea
- Class- Larvacea (appendicularia)
Class-Ascidiacea
- These are sedentary tunicates.
- The body is covered by a test.
- The pharynx is large and contains gill slits.
- Notochord, nerve cord, and tail are absent in adults.
- These are bisexual animals.
- Life history includes a typical tadpole larva.

Internal Structure of Ascidia – urochordate
The class Ascidiacea is divided into two orders.
Order 1. Enterogona
- These ascidians bear one gonad in the intestinal loop. The neural gland is ventral to the ganglion. Tadpole larva is seen.
- Ex: Ascidia and Ciona
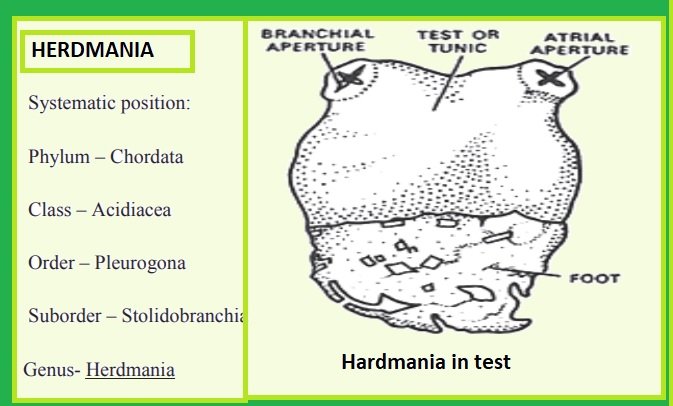
Order: 2. Pleurogona
In these ascidians, gonads are paired and are present in the atrial wall. The neural gland is dorsal to the ganglion:
Ex: Herdmania, Botryllus.
Class- Thaliacea
Characters of Thaliacea:
- These urochordates are free-swimming and pelagic forms.
- They are covered by the transparent test.
- The brachial and atrial apertures are placed at the anterior and posterior ends.
- The pharynx is small.
- Notochord, nerve cord, and tail are absent in the adult.
- Asexual reproduction is by budding.
- These are bisexual animals.
- Tailed larvae may be present or absent.
- Alternation of generations can be seen in life history.
The class Thaliacea is divided into three orders:
- Doliolida (Cyclomyarla) : Ex: Doliolum
- Pyrosomlda: Ex: Luminescent colonial form.
- Salpida (Hemimyaria): Ex: Salpa
Class – Larvacea (appendicularia):
Class Larvacea shows the following features:
- These are free-swimming pelagic tunicates.
- True test covering is lacking.
- They show a loose gelatinous house.
- This house is useful for filter feeding.
- Two-gill slits are present
- Atrium absent
- Notochord and nerve cord are persistent
- They show tail throughout their life.
- Neotenic forms are included.
- Ex: Oikopleura.
You Can also read:
- Characteristics and Classification of Phylum- Chordata
- Animal Kingdom – Classification
- Phylum – Porifera
- Phylum – Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
- Phylum- Ctenophora
- Phylum- Platyhelminthes
- Aschelminthes,
- Phylum-Annelida
Thank you 🙂



9 Comments
Characteristics and Classification of Phylum Chordata - PCSSTUDIES - · July 22, 2021 at 9:28 pm
[…] 1.Urochordata or Tunicata– Notochord is present only in the larval tail. Example- Ascidia, Salpa, Doliolum. […]
Scoliodon - Dogfish, Classification and Characteristics - PCSSTUDIES · September 6, 2021 at 10:32 am
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]
Migration in Fishes - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Migration in Fishes · September 8, 2021 at 1:49 am
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]
General Characters of Uromastyx - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · November 20, 2021 at 7:59 pm
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]
Neoteny in Amphibians - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · December 26, 2021 at 12:46 am
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]
Characters of Archaeopteryx - PCSSTUDIES Biology · March 30, 2022 at 8:53 am
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]
Herdmania- Sea Squirts - PCSSTUDIES Zoology Herdmania- Sea Squirts · April 26, 2022 at 6:14 am
[…] Sub Phylum – Urochordata, Tunicata […]
Pigeon (Columba livia) - General Characters - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · May 7, 2022 at 2:15 pm
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]
Parental Care in Amphibians - PCSSTUDIES Biology · June 13, 2022 at 11:18 am
[…] Subphylum – Urochordata […]