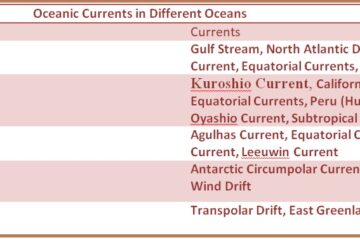
Oceanic Currents in Different Oceans
Oceanic Currents in Different Oceans Here’s an overview of the major oceanic currents in different oceans: Atlantic Ocean Currents The Atlantic Ocean has several important currents, most of which are part of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) system. Gulf Stream: One of the most well-known currents, the Gulf Stream Read more…