Muscular Tissue
Muscular Tissue
The Muscle tissue is soft and it makes different types of muscles in animals, which gives the ability of muscles to contract. Muscular tissues are also referred to as myopropulsive tissue.
- Muscular tissues are formed during embryonic development by the process of myogenesis.
- The muscle tissues are mesodermal in origin except for the ciliary muscles of the eyes which are of ectodermal origin.
- The study of Muscles is called Myology.
- The muscle cells are elongated, slender, and spindle-shaped, fiber-like cells.
- The muscle tissue contains contractile proteins called actin and myosin which meant movent by contraction and relaxation of muscles.
- So the primary function of muscle tissue is contraction, all three muscular tissues use the movement of actin against myosin to create contraction
Types of Muscular Tissues
The muscular tissues are differentiated into three types:
- Striated or skeletal muscle tissue
- Non-striated or smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
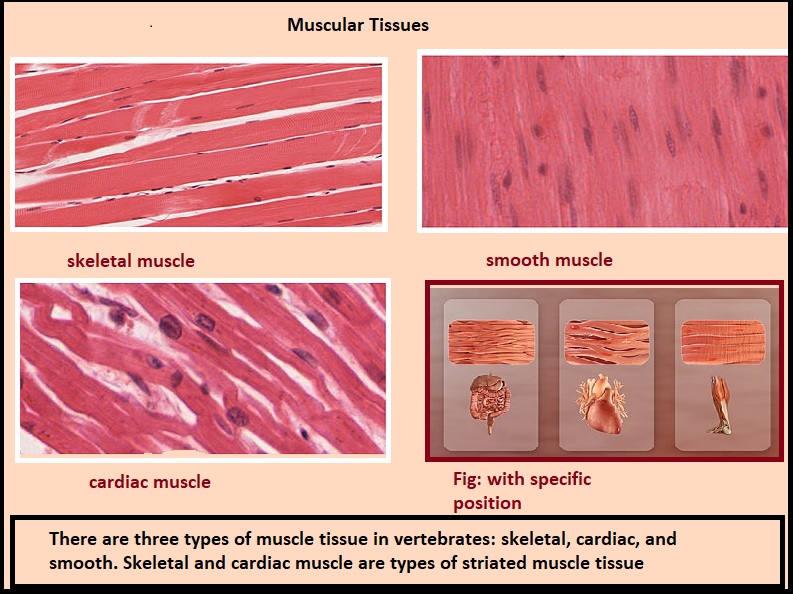
Muscle tissues: Cardiac muscles, skeletal muscles, and smooth muscles
Comparison of Muscular Tissues
A comparison of the three muscular tissues in the table is given below:
Striated or skeletal muscle tissue |
Non-striated or smooth muscle |
Cardiac muscle |
| The strait muscles consist of elongated muscle cells called muscle fibers which are responsible for the movements of the body. The striated muscle only contracts voluntarily, upon the influence of the central nervous system | Smooth muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention | Cardiac muscle also contracts involuntarily, without conscious intervention. It is self-contracting, autonomically regulated, and must continue to contract in a rhythmic fashion for the whole life of the organism. |
| An average adult human male is made up of 42% of skeletal muscle as a percentage of body mass, and an average adult human female is made up of 36%. All skeletal muscle and many smooth muscle contractions are facilitated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. | It is non-striated and involuntary and found within the walls of organs and structures such as the esophagus, stomach, intestine, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels, and the arrector pili in the skin which controls the erection of body hair | Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the walls of the Heart as Myocardium and is involuntarily being controlled by the autonomic nervous system. |
| Location of tissue: located in limbs, tongue, pharynx, etc | esophagus, stomach, intestine, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, and blood vessel (found in the walls of all visceral organs) | found only in the walls of the Heart as Myocardium |
| The tissues are multinucleated, with peripheral nuclei | These are uninucleated with the central nucleus. | These are uninucleated with the central nucleus |
| Shape and Size: Striated or skeletal muscle tissue is Long and cylindrical with the blunt ends | Non-striated or smooth muscle is short, spindle-shaped with pointed ends. | Cardiac muscles- these are short, cylindrical consisting of flat ends. |
| the sarcomere is present, max. length 3.7 µm | none | the sarcomere is present, max. length 2.6 µm |
| These are highly vascular tissues | These are less vascular tissues | These are highly vascular tissues. |
You can also Read:
Thank you 🙂


2 Comments
Classification of Animal Tissues - PCSSTUDIES - Biology - · June 30, 2021 at 12:00 pm
[…] Muscular tissue […]
Nervous Tissue - PCSSTUDIES - Biology - Nervous Tissue · December 11, 2022 at 2:47 pm
[…] Muscular Tissue […]