Phylum Platyhelminthes
Phylum Platyhelminthes
(Greek; platys= Flat; helmins = worms); The flatworms.
Phylum Platyhelminthes includes 13000 species. These are found as free-living as well as parasitic life forms. These are also called Flatworms because of having a dorso-ventrally flattened body.
Characteristics features of Phylum Platyhelminthes
The Platyhelminthes are mostly parasitic and live on or inside the host. A few are free-living and aquatic. The body of flatworms is thin, soft, unsegmented, and dorsoventrally flattened. They may be leaf-like or ribbon-like animals.
- These are mostly endoparasites, found in various animals including human beings.
- Symmetry: These are Bilaterally symmetrical.
- Germinal layer: triploblastic animals.
- Triploblastic– In a developing embryo, the third germinal layer called mesoderm is found in between ectoderm and endoderm. These animals are called triploblastic animals
- The body cavity: Acoelomate animals
- Level of organization: The organ level of organization is found.
- In parasites the hooks and suckers are present.
- Some parasitic organisms absorb nutrients directly from the host body’s surface.
- Hermaphrodites ( bisexual or monoecious) Sexes are not separate, internal fertilization.
Special Characters:
Flame cells:
Flame cells are the specialized in this phylum which helps in osmoregulation and excretion. Chief excretory waste is ammonia in Platyhelminthes.
Power of regeneration:
Some members of this phylum possess a high regeneration capacity. e.g., in Planaria.
Larval statges in Platyhelmithes
- The development in Platyhelminthes occurs through many larval stages. for example, the life cycle of fasciola includes miracidium larva, sporocyst larva, redia larva, cercaria larva, and metacercaria larva.
- The larval forms of Taenia are hexacanth larva and cysticercus larva.
Examples of Platyhelminthes:
Parasites: Fasciola hepatica (Liver fluke), Taenia (Tapeworm), Schistosoma (Blood fluke)
Taenia solium: also called pork tapeworm and found in all countries where the consumption of pork occurs. The larva of this organism is found in the pig’s muscles. Taenia solium lives as a parasite in the intestine of the human. It is a hermaphrodite organism and it undergoes self – self-fertilization.
Fasciola: Also called the liver fluke, it lives in the bile duct of sheep and goats. It is also hermaphrodite but in these organisms cross-fertilization takes place.
Schistosomes: These are called blood flukes because found in mesenteric blood vessels and the hepatic portal system of humans. It shows well-marked sexual dimorphism. They spread many diseases by contaminating the water.
Free-living: Planaria
planaria- It is found in freshwater. The Body comprises cilia and has the power to regenerate the lost part. They possess a pair of eyes and two lateral lobes.
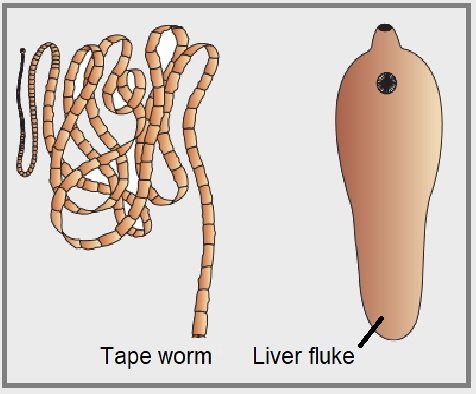
Examples of Platyhelminthes
Classification of Phylum Platyhelminthes:
The Platyhelminthes can be divided into:
- Turbellaria
- Trematoda
- Cestoda
Turbellaria:
Characteristic features of Tuberllaria:
- These are mostly found in fresh-water
- These animals are free-living
- Hooks and suckers are absent
- For example; Planaria, Otoplana
Trematoda
Characteristic features of Trematoda:
- The animals are mostly parasitic
- Presence of Hooks and suckers
- Example: Fasciola hepatica, Diplozoon
Cestoda
Characteristic features of Cestoda:
- The members are the exclusively parasitic
- presence of hooks and suckers
- Example: Taenia sps. Convoluta
You can also read: 💡
Thank you 🙂


16 Comments
Animal kingdom - Classification PCSSTUDIES - Biology - · May 29, 2021 at 2:32 pm
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum-Echinodermata - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % · June 15, 2021 at 7:29 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum- Ctenophora - PCSSTUDIES - Biology - Phylum- Ctenophora · June 15, 2021 at 7:33 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum-Mollusca - PCSSTUDIES - Biology - Phylum-Mollusca · June 15, 2021 at 7:48 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum-Arthropoda - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Phylum-Arthropoda · June 15, 2021 at 8:20 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum Aschelminthes - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % · July 13, 2021 at 3:00 pm
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]
PCSSTUDIES - Characteristics and Classification of Phylum Chordata % - · July 17, 2021 at 3:03 pm
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]
Amphioxus (Lancelet) - PCSSTUDIES - Science Amphioxus (Lancelet) · July 22, 2021 at 2:33 am
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum-Hemichordata - PCSSTUDIES - Biology % · July 22, 2021 at 8:02 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Balanoglossus - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Balanoglossus · August 10, 2021 at 7:32 am
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Petromyzon (Lamprey): General Characters - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · December 23, 2021 at 9:21 pm
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum - Porifera - PCSSTUDIES - Zoology · March 22, 2022 at 5:58 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Subphylum - Urochordata - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · May 7, 2022 at 2:54 pm
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum - Coelenterata (Cnidaria) - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · June 13, 2022 at 11:32 am
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Phylum-Annelida - PCSSTUDIES - Biology Phylum-Annelida · October 5, 2023 at 12:10 pm
[…] Phylum Platyhelminthes […]
Taxonomy - PCSSTUDIES - Biology · October 9, 2023 at 12:23 pm
[…] Phylum- Platyhelminthes […]